Medical History:
A 30-year-female patient presented to our clinic complaining of decreased vision in the left eye.
Diabetes mellitus (-)
Systemic hypertension (-)
Family history (-)
Smoking (-)
Trauma (-)
Examination Findings
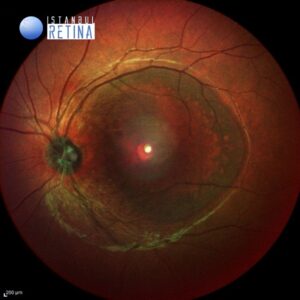
Best corrected visual acuity was 10/10 in the right eye and counting fingers at 3 meters in the left eye. Intraocular pressure was 15 mmHg in the right eye and 16 in the lefte ye. Anterior segment examination was unremarkable. Dilated funduscopic examination revealed normal fundus appearance in the right eye and temporal optic disc pit and shallow serous retinal detachment extending from the optic nerve to the macula in the left eye (Fig. 1).
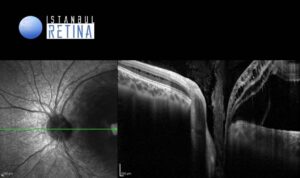
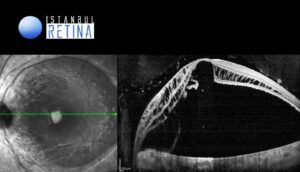
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) demonstrated condensed vitreous/glial tissue attached to the optic disc pit (Fig 2), and subretinal fluid and schisis-like inner retinal separation (Fig 3).
Diagnosis
Optic Disc Pit Maculopathy
Optic disk pit is a rare congenital abnormality of the optic nerve head. The incidence of optic disk pit has been reported about one in 10,000 without gender predilection. Vision is typically unaffected, while reduction in vision may occur in a frequency ranging from 25% to 75%, when serous macular detachment appears. Regarding the pathophysiology of optic disk pit maculopathy and the origin of fluid, the exact mechanism remains unclear.
Optic pits are generally found inferotemporally within the nerve, however up to one-third are central. Sub-retinal fluid, or macular schisis are complications that can be detected with a macular OCT.
Differential Diagnosis
Central serous retinopathy and macular neovascularization
Treatment
The management of optic disc pit maculopathy remains challenging. Although there have been reported some cases of spontaneous resolution, current management of optic disc pit maculopathy involves several approaches.
Laser photocoagulation treatment: the technique includes laser application temporal to the disc area to create a barrier for fluid not to enter the macula.
Surgical management: the most commonly used treatment alternative for optic disc pit maculopathy is vitrectomy, either alone or in combination with other treatment modalities, such as gas tamponade or laser photocoagulation. Studies have shown promising long-term results in both retinal attachment (50-95% of patients) and visual improvement (>50% of patients).
References:
- Karacorlu M, Sayman Muslubas I, Hocaoglu M, Ozdemir H, Arf S, Uysal O. Long-term outcomes of radial optic neurotomy for management of optic disk pıt maculopathy. Retina. 2016;36:2419-2427. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27579729/
- Chatziralli I, Theodossiadis P, Theodossiadis GP. Optic disk pit maculopathy: current management strategies. Clin Ophthalmol. 2018;12:1417-1422. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30127591/


