Medical History:
A 41-year-female patient presented to our clinic for an annual examination.
Diabetes mellitus (-)
Systemic hypertension (-)
Family history (-)
Smoking (-)
Trauma (-)
Examination Findings
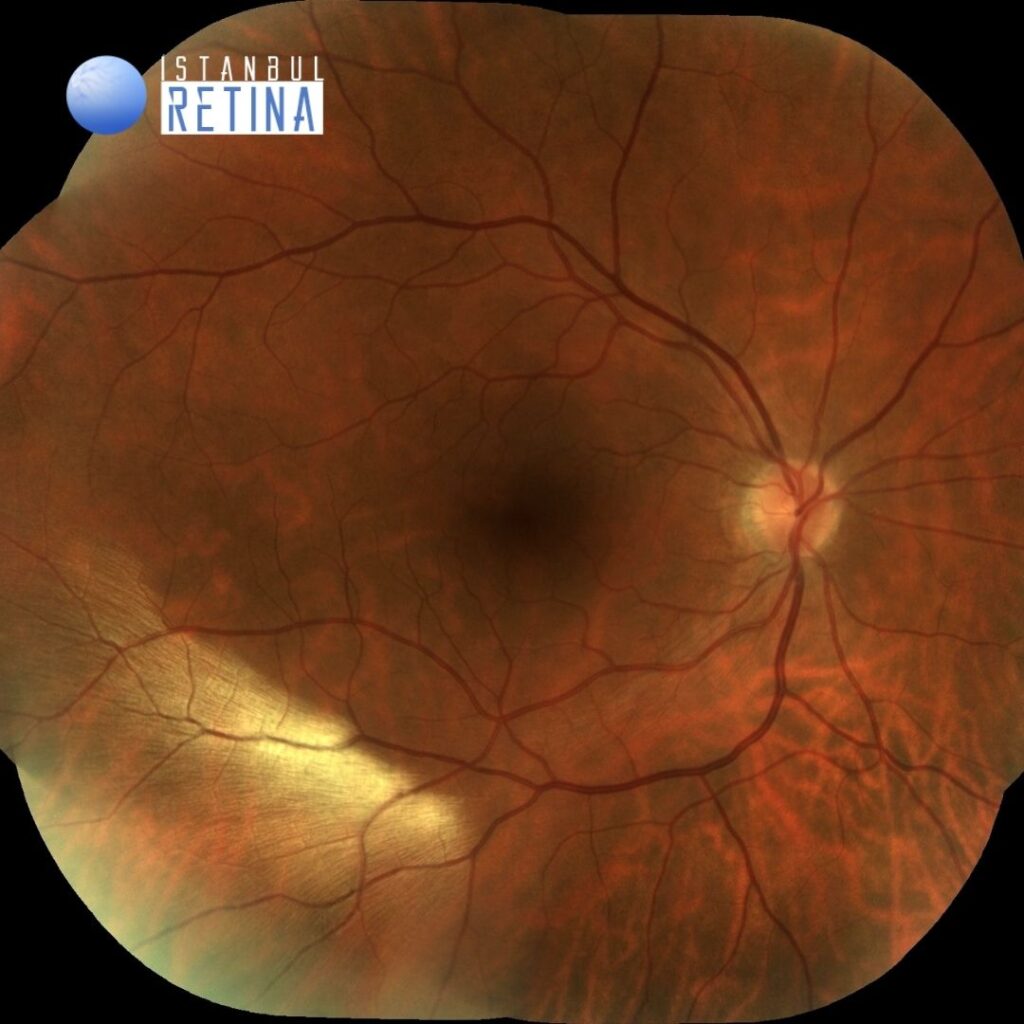
Best corrected visual acuity was 10/10 in the right eye and 10/10 in the left eye. Intraocular pressure was 13 mmHg in the right eye and 12 in the lefte ye. Anterior segment examination was unremarkable. Funduscopic examination revealed a white striated patch infero-temporal to the macula in the right eye (Figure 1).
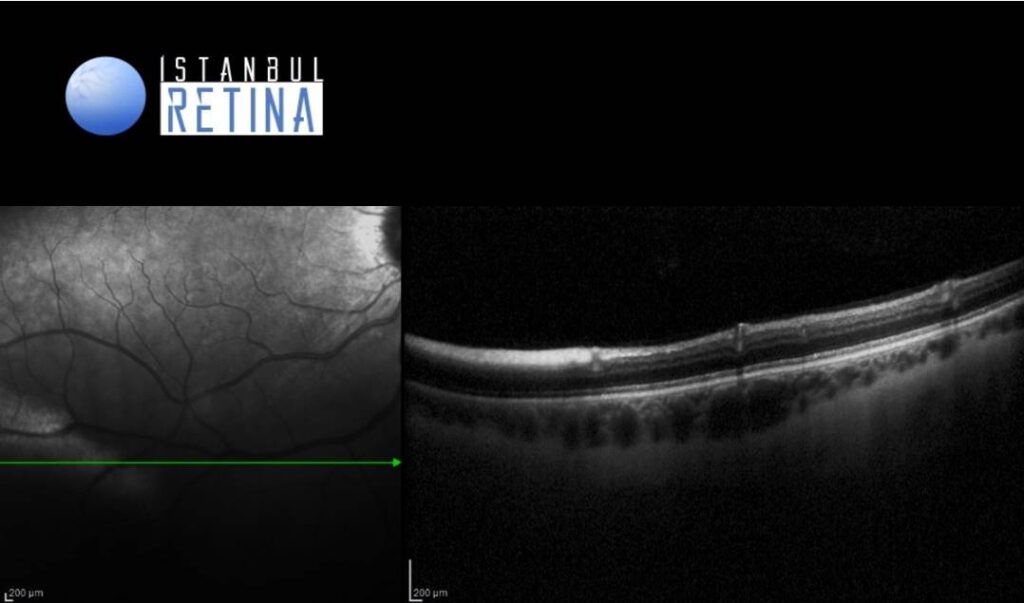
The spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan passing through the lesion identifies a thickened and hyperreflective retinal nerve fiber layer (Figure 2).
Diagnosis
Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers (RNFL) are rare developmental anomalies. They are retinal nerve fibers anterior to the lamina cribrosa that, unlike normal retinal nerve fibers, have a myelin sheath. Myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers are present in about 1% of the population and can occur bilaterally in approximately 7% of affected patients. Myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers are typically present at birth and are static lesions. Most patients with myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers are asymptomatic; however, some patients have associated ocular findings including axial myopia, amblyopia, and strabismus.
The majority of cases are diagnosed incidentally by ophthalmoscopy. On fundus examination they appear as white well-demarcated patches on the anterior surface of the neurosensory retina. On infrared imaging, myelinated RNFL appears white, which is likely due to the high lipid content of myelin. Myelin blocks detection of underlying fluorescent material and autofluorescence imaging reveals hypoautofluorescent area in the region of the myelinated RNFL. On optical coherence tomography (OCT), myelinated RNFL appears as a thickened and hyperreflective RNFL.
Differential Diagnosis
Neoplastic infiltrate, retinal vascular occlusion, cotton wool spot, retinoblastoma, chroiditis, retinitis, chorioretinal coloboma
Treatment
Myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers are typically benign lesions. Management of myelinated retinal nerve fiber layers is focused on serial eye examinations assessing for and treating associated conditions.
References:
1. Rao R, Turkoglu EB, Say EAT, Shields CL. Clinical Features, Imaging, and Natural History of Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer. Retina. 2019;39(6):1125-1132. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29443798/
2. Ramkumar HL, Verma R, Ferreyra HA, Robbins SL. Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL): A Comprehensive Review. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2018;58(4):147-156. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30239369/